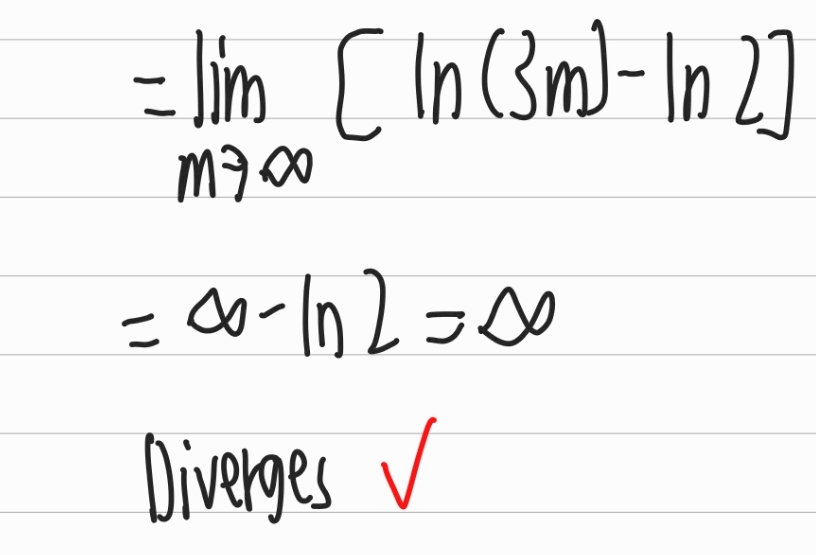
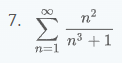
We use the Integral Test here which is:
If \(\int_1^\infty f(x) \, dx\) convergent, then \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} a_n\) is convergent.
If \(\int_1^\infty f(x) \, dx\) convergent, then \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty} a_n\) is divergent.
Then you basically take the \(\lim_{m \to \infty} \int_1^m f(x) \, dx\) which in this case is \(\frac{n^2}{n^3+1}\).
You proceed to take the integral and then finally taking the limit.
Since the limit does not equal to 0, it diverges which is the final answer.